How to Choose the Right SMAW Welding Machine for Your Workshop

Shielded Metal Arc Welding, commonly known as SMAW or manual metal arc welding, remains one of the most widely used welding processes across industries. From fabrication shops to onsite maintenance work, SMAW continues to be the benchmark process for reliability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness.
Choosing the right SMAW welding machine, however, depends on more than just amperage ratings or price. It comes down to understanding your application, power availability, portability needs, and long-term operating costs.
Let’s break it down.
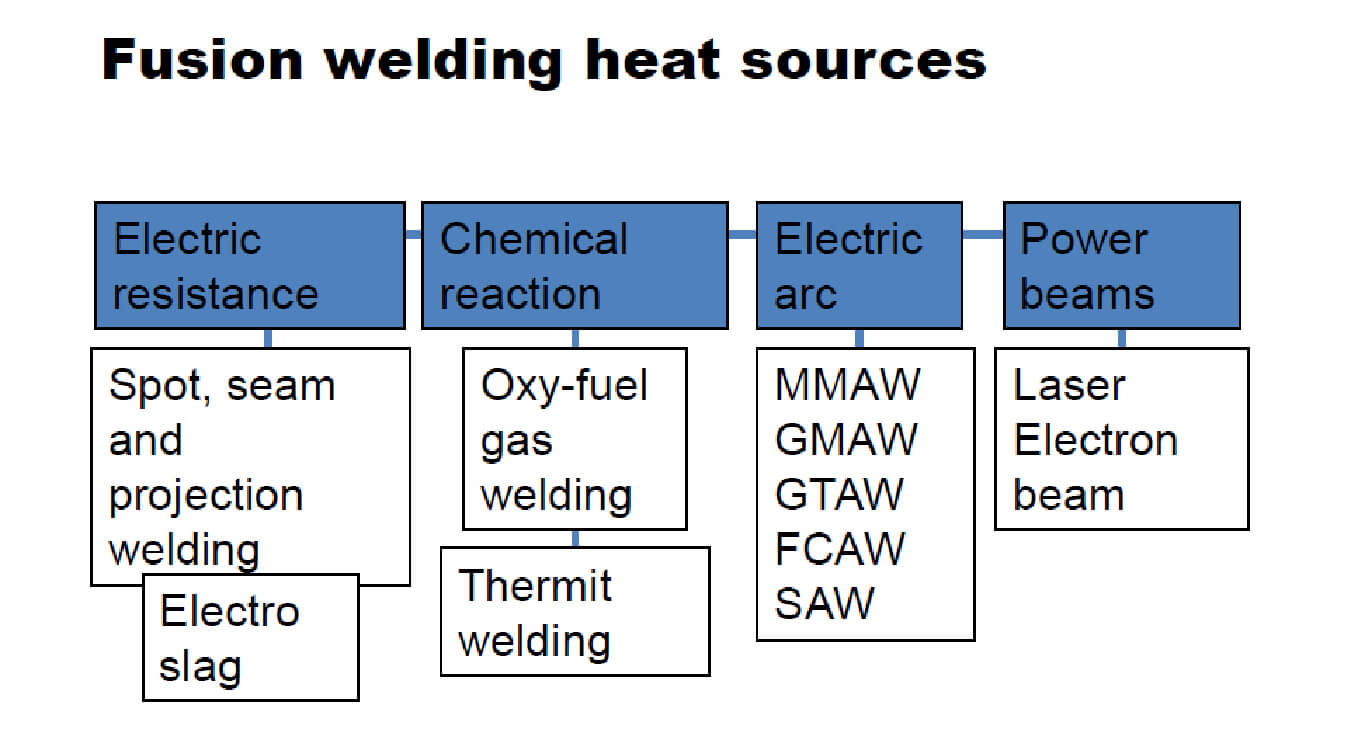
Understanding the SMAW Welding Process
SMAW is a fusion welding process where heat is generated by an electric arc formed between a consumable electrode and the workpiece. The arc melts both the base metal and the electrode, forming a weld pool protected by flux-based slag.
To achieve this, the welding power source must deliver:
- High current typically in the range of 50–300 A.
- Low voltage generally between 10 and 50 V.
- A stable arc for consistent metal transfer.
Since industrial power supplies operate at much higher voltages (230 V or 400 V), welding machines rely on transformers and electronic controls to reduce voltage and regulate current. For DC welding, rectification is required.
Common Heat Sources Used for Fusion Welding
While multiple heat sources exist for joining metals, SMAW remains one of the most commonly used methods due to its simplicity and adaptability. It is especially effective in environments where access, weather conditions, or power stability may be a challenge.
Key Features of SMAW Welding Equipment
SMAW welding machines are widely preferred because they offer:
- High portability and operational flexibility.
- Applicability across a wide range of materials, joints, and welding positions.
- Capability to deposit approximately 1 kg of weld metal per hour.
- Excellent mechanical and metallurgical properties when executed correctly.
- Proven reliability as a benchmark industrial welding process.
That said, SMAW does require skilled operators to achieve consistent weld quality.
Advantages of SMAW Welding Machines
From a workshop or site perspective, SMAW offers several practical advantages:
- Simple welding process with portable equipment.
- Relatively low equipment cost.
- Wide availability of electrodes for different metals and alloys.
- Ability to weld carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel, and cast iron.
- Suitable for all welding positions.
- Effective for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- Allows longer welding cable lengths compared to many other processes.
These advantages make SMAW especially suitable for maintenance, repair, and fabrication work.
Types of SMAW Welding Machines and Power Sources
Understanding the different types of SMAW power sources is key to selecting the right machine for your workshop.
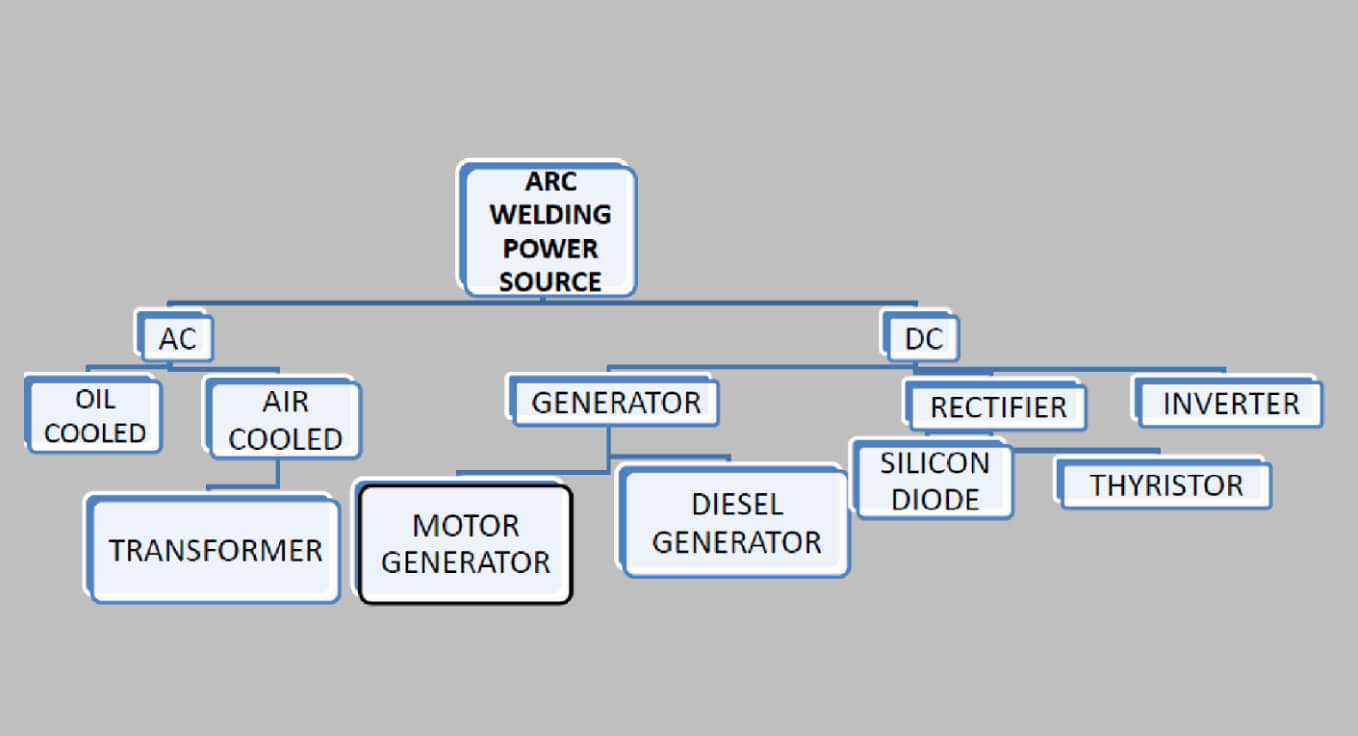
1. Welding Transformer
A welding transformer is the most basic form of SMAW equipment. It works as a step-down transformer, reducing the mains voltage to a safe and usable welding voltage.
Best suited for:
- Basic fabrication work
- Workshops with stable AC power
- Cost-sensitive applications
Limitations:
- AC output only
- Less arc stability compared to DC machines
2. Motor Generator Welding Machine
In a motor generator system, the input electrical power drives an induction motor connected to a generator. Mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy, producing a DC output through carbon brushes and a commutator.
Key benefits:
- Very stable DC
- Smooth arc characteristics
Diesel Generator Variant:
Diesel-driven generators are widely used for on-site and remote welding jobs where grid power is unavailable.
Limitations:
- Higher maintenance
- Larger footprint
- Higher operating costs
3. Welding Rectifier
Welding rectifiers combine a transformer with silicon diode-based rectifiers to convert AC into DC.
Key Benefits:
- Reliable DC output
- Better arc stability than transformers
- Suitable for a wide range of electrodes
This remains one of the most commonly used SMAW power sources in industrial environments.
4. Welding Inverter
Inverter welding machines represent the latest evolution in SMAW power sources. The process involves:
- Converting AC input to DC
- Transforming DC into high-frequency AC
- Converting it back into a controlled DC output
This allows precise control over welding parameters through electronic and software-based systems.
Key Benefits:
- High energy efficiency
- Significant weight and size reduction
- Excellent arc stability and weld quality
- Lower power consumption
Because of these benefits, inverter-based SMAW machines are now the preferred choice across most industrial sectors.
SMAW Welding Solutions from Ador Welding
At Ador, SMAW solutions are designed to meet diverse industrial needs. The portfolio includes:
- Robust welding transformers
- Thyristor-controlled rectifier machines
- Power-efficient inverter-based SMAW machines
Each solution is engineered to deliver reliability, performance, and long service life. The choice of equipment is guided by application-specific requirements, ensuring optimal results and customer satisfaction.